
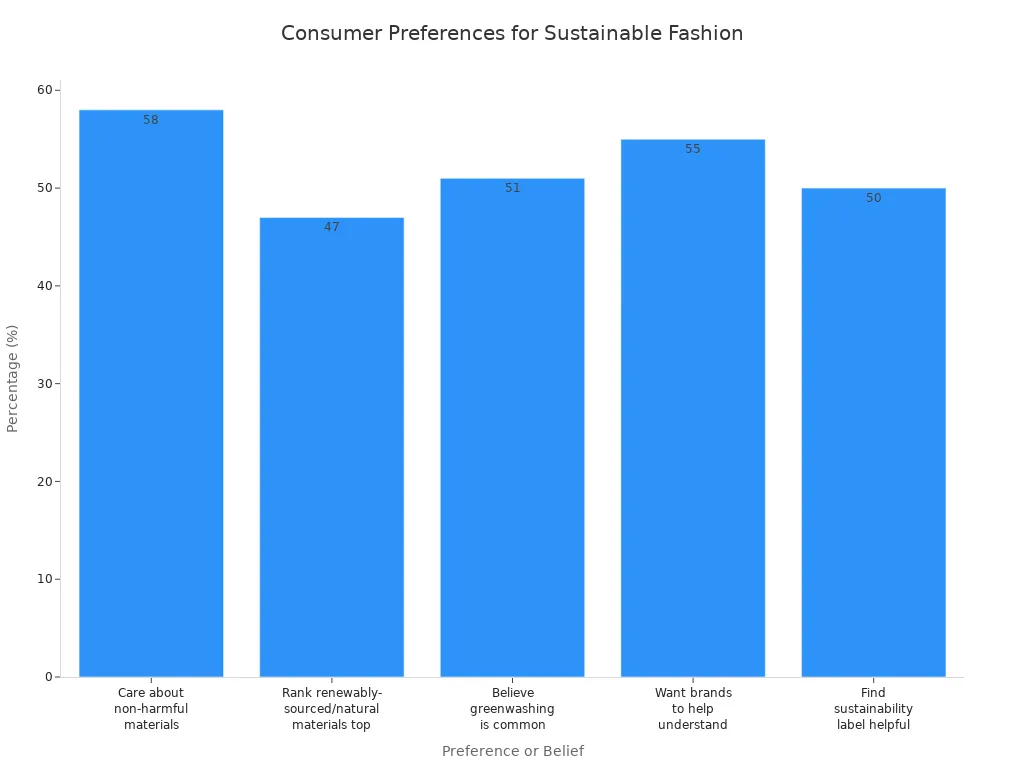
Sustainability has become a crucial aspect of the fashion industry today. With consumers increasingly valuing eco-friendly practices, brands must adapt to these changing preferences. Recent surveys reveal that 58% of consumers care about non-harmful materials, while 47% prioritize renewable or natural sources. This shift underscores the alignment of sustainable knitted fabrics with consumer values, making them essential for modern collections. Furthermore, innovation plays a pivotal role in enhancing these fabrics, driving the industry toward a more sustainable future.
Key Takeaways
- Sustainable knitted fabrics align with consumer values, as 58% prioritize eco-friendly materials. Brands must adapt to these preferences to stay relevant.
- These fabrics offer significant environmental benefits, including reduced carbon footprints and water conservation, making them a responsible choice for fashion brands.
- Investing in sustainable fabrics can lead to long-term savings. Durable garments reduce the need for frequent replacements, making them cost-effective over time.
- Brands should focus on transparency in their sustainability efforts. Communicating successes and challenges builds trust with consumers and enhances brand reputation.
- Innovative technologies like 3D knitting and microbial dyeing are shaping the future of sustainable fabrics, reducing waste and improving production efficiency.
Benefits of Sustainable Knitted Fabrics

Sustainable knitted fabrics offer numerous advantages that extend beyond mere aesthetics. These benefits encompass environmental, economic, and social dimensions, making them a compelling choice for brands aiming to enhance their collections.
Environmental Benefits
Sustainable knitted fabrics significantly reduce the environmental impact of fashion. The following table outlines key environmental benefits:
| Environmental Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Carbon Footprint | Sustainable fabrics like organic cotton and hemp derive from renewable resources, leading to lower carbon emissions compared to synthetic fibers. |
| Water Conservation | These fabrics significantly lower water consumption, with organic cotton relying more on rainwater than irrigation. |
| Mitigation of Chemical Contamination | Sustainable fabrics utilize organic farming techniques and eco-friendly dyes, reducing harmful chemical usage in production. |
| Fostering Biodiversity | Sustainable textiles promote practices like crop rotation, enhancing soil vitality and supporting diverse ecosystems. |
| Waste Reduction | Sustainable fabrics are often more durable and biodegradable, reducing the frequency of garment disposal and long-term waste. |
| Energy Efficiency | The production of sustainable fabrics typically requires less energy than conventional textile manufacturing. |
| Promotion of Ethical Practices | Sustainable fabric manufacturing ensures better working conditions and fair wages for workers, contributing to social sustainability. |
| Circular Economy | These fabrics support a circular economy by enabling recycling and upcycling, minimizing waste and resource demand. |
| Increased Environmental Awareness | The rise of sustainable fabrics fosters greater awareness among consumers about the environmental impact of their clothing choices. |
Economic Benefits
Adopting sustainable knitted fabrics can also yield economic advantages for brands. Although the initial investment may be higher, the long-term savings are substantial. For instance, sustainable garments often last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements. A comparison of costs illustrates this point:
| Type of Shirt | Cost | Lifespan (wears) | Cost per Wear |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Shirt | $120 | 100+ | $1.50 |
| Fast Fashion Shirt | $30 | 10-15 | $3.00 |
Social Benefits
Sustainable knitted fabrics contribute to social sustainability by promoting ethical labor practices. Brands that prioritize these fabrics often engage with suppliers who adhere to fair labor standards. This commitment not only enhances brand reputation but also fosters consumer trust.
“Sustainable knitwear can be counted among the most dynamic means of lessening the impact that your clothes have on the planet.”
This quote highlights the transformative potential of sustainable fabrics in reducing the fashion industry’s carbon footprint. By choosing sustainable options, brands can align their values with those of environmentally conscious consumers.
Key Materials in Sustainable Knitting

Sustainable knitted fabrics utilize a variety of materials that contribute to environmental conservation and ethical production practices. The following materials stand out as the most widely used in sustainable knitting:
- Recycled yarns
- Organic cotton
- Polyester
- Viscose
- Modal
- Bamboo
Organic Cotton vs. Conventional Cotton
Organic cotton represents a significant advancement over conventional cotton in terms of environmental impact. The table below highlights key differences:
| Aspect | Organic Cotton | Conventional Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Water Use | 91% less blue water | 2,700 liters per T-shirt |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | 46% fewer emissions | High emissions |
| Pesticide Use | No synthetic pesticides | 4% of global pesticides |
| Chemical Toxicity | Reduced by up to 90% | High toxicity |
| Soil Health | Improved due to organic practices | Degradation and loss of fertility |
| Health Risks | Fewer health issues reported | 48% of farmers report poisoning |
Organic cotton farming employs natural insecticides, avoiding synthetic chemicals altogether. This practice not only reduces health risks for farmers but also conserves water by prioritizing rain-fed irrigation. In contrast, conventional cotton practices contribute to soil degradation and biodiversity loss.
The Role of Recycled Fibers
Recycled fibers play a crucial role in enhancing the sustainability of knitted fabrics. They decrease the need for virgin materials, thus minimizing waste and fostering a circular economy. The table below illustrates the types of recycled fibers commonly used:
| Type of Recycled Fiber | Percentage in Yarn | Suitability for Knit Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-consumer recycled cotton | Up to 25% | Yes |
| Post-consumer recycled cotton | Up to 10% | Yes |
By transforming discarded garments into new fabric, recycled fibers mitigate the environmental impacts linked to conventional fabric production, such as excessive water use and greenhouse gas emissions.
Performance Characteristics of Alternative Fibers
Bamboo, hemp, and TENCEL™ are notable materials in sustainable knitted fabrics. Bamboo is celebrated for its softness and versatility, especially when processed through closed-loop systems like lyocell. This method enhances its sustainability. Hemp, on the other hand, is recognized for its durability and minimal chemical processing, making it an excellent choice for sustainable knitting. Both fibers offer unique benefits: bamboo provides moisture-wicking properties and odor resistance, while hemp is known for its strength and eco-friendliness.
Challenges in Sourcing Sustainable Materials
While the benefits of sustainable materials are clear, challenges exist in sourcing and processing them. Key challenges include:
- New standards for recycled fibers are necessary to ensure quality.
- Existing spinning processes must be adapted for recycled materials.
- Regulatory ambiguity regarding hemp can impede its market growth.
- High production costs are a significant barrier for sustainable materials.
- Processing methods for bamboo can have detrimental environmental impacts.
These challenges highlight the need for ongoing innovation and collaboration within the industry to enhance the sustainability of knitted fabrics.
Integrating Sustainable Fabrics into Collections
Integrating sustainable knitted fabrics into collections requires strategic planning and execution. Brands can adopt several effective methods to ensure a seamless transition. Here are some successful approaches:
- Utilize Recycled Materials: Brands like Fisher Textiles incorporate recycled polyester in their products. Their ET9848 EZ Stretch Premium is made from 100% post-consumer recycled polyester, diverting PET bottles from landfills.
- Adopt Certified Yarns: Berger Textiles offers the EVO line, which uses GRS-certified recycled yarn. This ensures a minimum of 50% recycled content, significantly lowering carbon footprints compared to standard fabrics.
- Implement Water-Saving Processes: Aberdeen Fabrics, Inc. utilizes the CleanRTex process, which reduces water consumption by 90% and generates zero wastewater.
Despite these opportunities, brands face challenges when integrating sustainable fabrics. High costs, lack of managerial knowledge, and insufficient local government support can hinder progress. Additionally, unclear sector-specific laws and regulations create uncertainty in sourcing sustainable materials.
To effectively market collections featuring sustainable knitted fabrics, brands should focus on transparency. They must communicate both successes and challenges in their sustainability journey. Highlighting ethical labor practices and promoting eco-friendly materials can resonate with environmentally conscious consumers.
Collaborations with sustainable fabric suppliers offer numerous benefits. These partnerships ensure ethical sourcing, provide access to innovative materials, and help brands reduce their environmental impact. Such collaborations also strengthen consumer relationships by building trust and loyalty.
By embracing these strategies, brands can successfully integrate sustainable knitted fabrics into their collections, aligning with consumer values and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Innovations in Sustainable Knitting
The textile industry is witnessing remarkable innovations that enhance the sustainability of knitted fabrics. These advancements not only reduce waste but also improve production efficiency. Here are some key technologies shaping the future of sustainable knitting:
-
3D Knitting: This technology allows manufacturers to create complex designs with minimal waste. By producing garments in a single seamless piece, 3D knitting eliminates fabric scraps, significantly reducing material waste. This method also lowers labor costs, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
-
Circular Knitting: Circular knitting machines produce fabrics quickly and efficiently. This technology minimizes waste by allowing for continuous production, which reduces the need for cutting and sewing. As a result, manufacturers can create high-quality knitted fabrics while conserving resources.
-
Microbial Dyeing: This innovative approach replaces synthetic dyes with bacteria-based pigments. Microbial dyeing eliminates toxic dye waste and reduces water consumption, making it a more eco-friendly option for coloring fabrics.
Utilizing digital knitting technologies leads to substantial sustainability benefits. These technologies minimize material waste by producing only what is necessary and eliminate excess stock through on-demand manufacturing. This approach supports waste reduction and encourages the creation of personalized products that consumers are likely to use longer.
Furthermore, the implementation of closed-loop production systems is gaining traction. This process involves collecting and sorting knitting fabric waste, shredding and cleaning it, and extracting fibers for reuse. The steps include:
- Collection and Sorting
- Shredding and Cleaning
- Fiber Extraction
- Fiber Reinforcement and Spinning
- Fabric Production
These systems significantly reduce waste sent to landfills and conserve resources. They also create economic opportunities by generating jobs in sustainable manufacturing.
As the market for sustainable knitted fabrics continues to grow, these innovations will play a crucial role in shaping a more sustainable future for the textile industry.
Sustainable practices in fashion are essential for the industry’s future. The fashion sector significantly impacts the environment, accounting for 2-8% of global carbon emissions and consuming vast amounts of water. Brands that adopt sustainable knitted fabrics can enhance their reputation and foster customer loyalty.
- Benefits of adopting sustainable fabrics:
- Enhanced brand reputation
- Increased customer loyalty
- Differentiation in a competitive market
By embracing sustainability, brands can contribute to a healthier planet and a more responsible textile industry.
FAQ
What are sustainable knitted fabrics?
Sustainable knitted fabrics are textiles made from eco-friendly materials. They minimize environmental impact through reduced water usage, lower carbon emissions, and ethical labor practices. These fabrics often include organic cotton, recycled fibers, and innovative materials like TENCEL™.
How do I know if a fabric is sustainable?
Look for certifications such as GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) or OEKO-TEX. These labels indicate adherence to environmental and social standards. Additionally, check for transparency in sourcing and production processes from the manufacturer.
Can sustainable fabrics be stylish?
Absolutely! Sustainable fabrics come in various textures, colors, and designs. Many brands prioritize aesthetics while maintaining eco-friendly practices, ensuring that consumers can enjoy fashionable garments without compromising their values.
Are sustainable knitted fabrics more expensive?
While the initial cost may be higher, sustainable knitted fabrics often provide long-term savings. Their durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, making them a cost-effective choice over time.
How can brands integrate sustainable fabrics into their collections?
Brands can start by sourcing certified materials, collaborating with sustainable suppliers, and adopting eco-friendly production processes. Transparency in marketing and educating consumers about the benefits of sustainable fabrics also plays a crucial role in successful integration.




