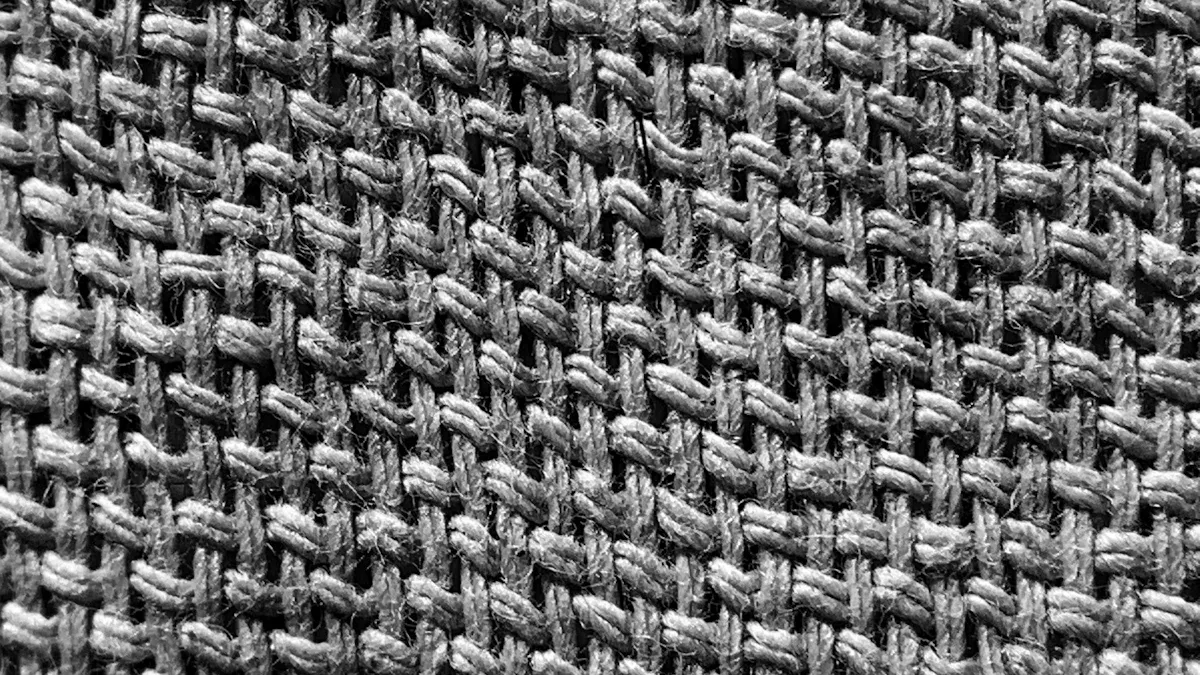
Knitted fabrics create clothing that feels stretchy and comfortable. You often find them in casual wear like t-shirts and sweaters. Woven fabrics, on the other hand, offer durability and structure. They work well for items like suits and bags. Your choice depends on how you plan to use the clothing.
Key Takeaways
- Knitted fabrics are stretchy and comfortable, making them ideal for casual and active wear like t-shirts and sweaters.
- Woven fabrics are strong and durable, perfect for structured clothing such as suits and formal dresses.
- Choose knitted fabrics for comfort and flexibility, while woven fabrics are better for durability and maintaining shape.
Understanding Knitted Fabric
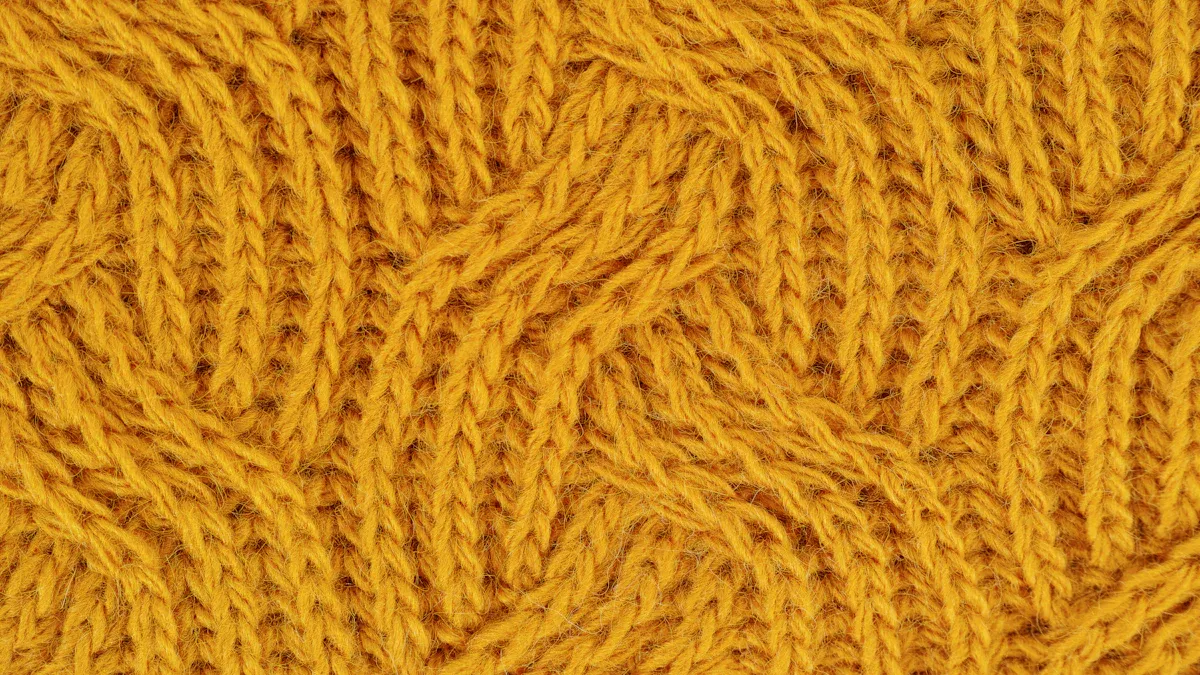

Definition and Characteristics
Knitted fabric consists of interlocking loops of yarn. This unique structure gives it a stretchy quality that enhances comfort. The elasticity of knitted fabrics allows them to adapt to your body’s shape, making them ideal for various clothing styles. Different knit structures, such as rib and jersey knits, offer varying levels of stretch and recovery. For example, rib knits are highly elastic, while jersey knits provide moderate stretch. The ability of these fabrics to return to their original shape after stretching is crucial for maintaining fit and comfort.
Here’s a quick overview of some common structural characteristics of knitted fabrics:
| Fabric Type | Structural Characteristics | Performance Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Plain | Balanced structure, high mass per unit area | Superior bursting strength |
| Rib | Higher stitch density | Lower air permeability |
| Interlock | Balanced structure, high mass per unit area | Superior bursting strength |
| Lace | Elongated stitches, low stitch density | Weakest bursting strength, highest air permeability |
| Double-bed Knits | Higher elasticity, better wrinkle recovery | Enhanced wrinkle recovery |
| Cardigan | Tuck stitches reduce elasticity | Low drapeability |
| Lacoste | Tuck stitches reduce elasticity | Low drapeability |
Common Uses in Clothing
You will find knitted fabrics in a variety of clothing items. Their stretch and comfort make them perfect for casual and active wear. Here are some common uses:
- Sweaters: Knitted fabrics provide warmth and comfort, making them a popular choice for sweaters.
- Cardigans: These often use cable knits, which offer both elasticity and style.
- Children’s Clothing: Purl knits are common in children’s wear due to their flexibility and comfort.
- Dresses: Jersey knits are frequently used for dresses, balancing style with comfort.
- Activewear: The stretch and body-conforming properties of knitted fabrics make them ideal for activewear.
Knitted fabrics not only enhance the fit of your clothing but also contribute to your overall comfort throughout the day.
Understanding Woven Fabrics

Definition and Characteristics
Woven fabrics consist of yarns interlaced together in a grid-like pattern. This unique structure gives woven fabrics their strength and durability. The tight interlacing of yarns creates a stable fabric that resists wear and maintains its shape over time. Here are some key characteristics of woven fabrics:
- Durability: The interlacing of yarns enhances strength and resistance to wear. This structure allows woven fabrics to maintain their shape and dimensions, preventing distortion and stretching.
- Tensile Strength: Woven fabrics exhibit high tensile strength due to the tight interlacing of yarns. This quality makes them ideal for clothing that requires durability.
- Variety of Textures: Woven fabrics can come in various textures and weights, making them suitable for different clothing styles and purposes.
Common Uses in Clothing
Woven fabrics find their place in many types of clothing. Their durability and structured nature make them ideal for formal and everyday wear. Here’s a table showcasing some common woven fabric types, their uses, and reasons for their popularity:
| Fabric Type | Common Uses | Reasons for Choice |
|---|---|---|
| Poplin | Shirts, dresses, blouses | Fine, tightly woven structure provides durability and comfort. |
| Twill | Denim, workwear | Diagonal weave offers strength and durability. |
| Muslin | Baby clothes, summer garments | Lightweight and breathable, ideal for warm weather. |
| Velvet | Jackets, pants | Soft texture adds aesthetic appeal. |
| Polyester | Fashion, sportswear | High durability, low maintenance, quick-drying properties. |
| Nylon | Socks, lingerie, outdoor gear | High strength, lightweight, and water-resistant. |
| Acrylic | Sweaters, scarves | Lightweight with thermal insulation, vibrant colors. |
Woven fabrics play a crucial role in your wardrobe. Their ability to provide structure and durability makes them a popular choice for a wide range of clothing items. Whether you need a sturdy pair of jeans or a stylish dress, woven fabrics have you covered.
Comfort Comparison
Breathability
Breathability plays a crucial role in your comfort when wearing clothing. Knitted fabrics generally offer moderate breathability, allowing air to circulate while keeping you cool. In contrast, woven fabrics often excel in this area. Laboratory tests show that laminated woven fabrics provide high breathability, making them suitable for warm weather. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Fabric Type | User Experience | Test Data (Breathability) |
|---|---|---|
| Knit fabric (Epic-treated) | Feels cool | Moderate |
| Woven fabric (laminated) | Feels firm | High |
When it comes to moisture management, knitted fabrics can vary. Studies indicate that knit structures with floats manage moisture better than those without. Tight-knit structures tend to trap air, which can hinder moisture-wicking abilities. This means that while knitted fabrics feel comfortable, they may not always keep you dry during intense activities.
Softness and Feel
Softness is another important factor in your clothing choices. Consumer surveys reveal that knitted fabrics often feel softer than woven ones. The perception of softness can significantly impact your comfort level. Here’s a summary of how different fabric types compare:
| Fabric Type | Softness Perception | Sensibility Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| Knit | 3.67 | Feminine, Sexy, Delicate, Romantic |
| Film | 2.83 | Genteel, Dignified, Masculine, Refined |
Knitted fabrics score higher in comfort due to their stretchability and softness. Woven fabrics, while durable and structured, may not provide the same level of comfort. You might find that knitted clothing feels more inviting against your skin, especially for everyday wear.
Durability and Maintenance
Wear and Tear Resistance
When it comes to wear and tear, woven fabrics generally outperform knitted ones. Woven fabrics have a structured nature that prevents stretching and wear, allowing them to last a lifetime. In contrast, knitted fabrics are thinner and more prone to stretching and tearing over time.
Here’s a quick comparison of abrasion resistance between the two fabric types:
| Fabric Type | Abrasion Resistance Result |
|---|---|
| Woven Fabric | Complete breakage of at least two separate yarns. |
| Knitted Fabric | Breakage of one yarn, resulting in a hole in the appearance. |
This table shows that woven fabrics can withstand more stress before showing signs of damage. Knit fabrics, while comfortable, can lose their shape and snag, leading to a shorter lifespan.
Care Instructions
Proper care can significantly extend the life of your clothing. Here are some recommended care instructions for both knitted and woven fabrics:
-
Knitted Fabrics:
- Hand washing is preferred to prevent stretching and pilling.
- Use a mild, wool-safe detergent with cold or lukewarm water to avoid shrinking.
- Never wring out knitwear; gently press out excess water and lay flat to dry.
-
Woven Fabrics:
- Gentle washing techniques, such as hand washing or using a delicate cycle, help maintain the fabric’s integrity.
- Avoid high heat during drying, as it can lead to damage and reduced lifespan.
- Turn garments inside out and use a mesh bag when machine washing to prevent stretching.
By following these care tips, you can ensure that your clothing remains in great condition for years to come.
Stretchability and Fit
Elasticity in Knitted Fabric
Knitted fabrics excel in elasticity due to their unique interlooped structure. This design allows the fabric to stretch significantly. When you pull a loop horizontally, it extends fully, while a vertical pull only stretches it halfway. This characteristic makes knitted fabrics ideal for clothing that requires flexibility and comfort.
Here’s a quick overview of how elasticity impacts garment fit and movement:
| Property | Impact on Garment Fit and Movement |
|---|---|
| Shape Retention | Maintains form and prevents sagging, ensuring a consistent fit over time. |
| Comfort and Flexibility | Enhances ease of movement, crucial for activewear and performance clothing. |
| Custom Fit | Conforms to various body shapes, providing a tailored fit for wearers. |
The rebound tension in knitted fabrics allows them to return to their original size after stretching. Fabrics with elastane improve this stretch memory, enhancing garment performance. However, low rebound tension can lead to garments losing their shape over time.
Structure in Woven Fabrics
Woven fabrics maintain their structure through tight interweaving of yarns. This stability makes them ideal for tailored garments like suits and formal dresses. Woven fabrics generally have limited stretch, which helps them retain their shape even after prolonged wear.
Here are some key features of woven fabrics that contribute to their fit:
- Woven fabrics maintain their shape and structure over time, making them ideal for tailored garments.
- The stable structure makes them easier to cut and sew, providing a solid base for intricate designs.
- Most woven fabrics exhibit a stable shape, supporting more tailored garments and formal wear.
The unique characteristics of woven fabrics ensure that they provide a crisp and defined silhouette, making them a popular choice for structured clothing.
Wrinkle Resistance
Performance of Knitted Fabrics
Knitted fabrics typically show lower wrinkle resistance compared to woven fabrics. Their stretchy nature allows them to recover from wrinkles, but they may not perform as well in practical situations. For example, polyester knits tend to outperform cotton knits in wrinkle recovery. After multiple washes and wears, polyester fabrics can maintain a wrinkle recovery angle of 85–95%. In contrast, cotton knits only achieve a recovery angle of 60–70%.
You can see how wrinkle resistance is measured in the table below:
| Test Method | Description | Test Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Wrinkle Tester | Determine the appearance of textile fabrics after induced wrinkling. | AATCC 128: Wrinkle Recovery of Fabrics- Appearance Method |
Performance of Woven Fabrics
Woven fabrics excel in wrinkle resistance due to their tightly interlaced structure. This stability helps them maintain a crisp appearance throughout the day. You will find that woven fabrics, such as cotton or polyester blends, resist wrinkling better than their knitted counterparts.
Here are some key points about woven fabrics and wrinkle resistance:
- Woven fabrics generally maintain their shape and resist creasing.
- They often require less ironing and upkeep compared to knitted fabrics.
- The structured nature of woven fabrics allows them to look polished and professional.
Fraying and Longevity
Fraying in Knitted Fabrics
Fraying in knitted fabrics occurs when threads unravel at the edges. This unraveling leads to a worn appearance and reduces durability. The interlaced threads in knitted fabrics lack support when cut, causing them to come loose. Here are some common causes of fraying in knitted fabrics:
- Cutting: When you cut knitted fabrics, the loops can unravel easily.
- Wear and Tear: Frequent use can weaken the threads, leading to fraying.
- Improper Care: Washing and drying methods can also contribute to fraying.
To prevent fraying, choose fabrics that resist it. You can also ensure proper finishing techniques during garment production. Techniques like double knitting can improve stability and reduce fraying, enhancing the longevity of your clothing.
Fraying in Woven Fabrics
Woven fabrics generally resist fraying better than knitted ones. Their tightly interlaced structure provides strength and stability. However, fraying can still occur, especially at the edges. Here are some factors that contribute to fraying in woven fabrics:
- Edge Finishing: Poorly finished edges can lead to fraying over time.
- Fabric Quality: Low-quality woven fabrics may fray more easily.
- Frequent Washing: Regular washing can weaken the threads, causing them to fray.
To maintain the longevity of woven fabrics, use proper care techniques. Always check the care label for washing instructions. By taking these steps, you can keep your clothing looking fresh and new for longer.
In summary, you should choose knitted fabrics for casual and active wear. They provide comfort and flexibility. Woven fabrics excel in formal and structured clothing, offering durability and shape. Ultimately, your best choice depends on your personal preference and the purpose of the clothing you need.
FAQ
What are the main differences between knitted and woven fabrics?
Knitted fabrics stretch and offer comfort. Woven fabrics provide durability and structure, making them suitable for different clothing types.
Can I use knitted fabrics for formal wear?
While you can use knitted fabrics for some formal wear, woven fabrics are generally better for structured and polished looks.
How do I care for knitted and woven fabrics?
For knitted fabrics, hand wash gently. For woven fabrics, use a delicate cycle and avoid high heat during drying to maintain quality.





